Low fidelity prototype or high fidelity wireframes? Which one should you choose and when? All the answers plus great examples! The fidelity spectrum for wireframes and prototypes is vast. The UX design workflow will typically include paper sketches, basic low fidelity wireframes and/or high fidelity, interactive wireframes or prototypes.
With smart technology thriving in the digital sphere, high fidelity wireframes offer designers powerful visual and interactive attributes to bring their designs to life. But this doesn’t mean that paper is dead. Low fidelity wireframes remain a quick, effective and practical design route – and this whimsical video shows us why paper should never be neglected.
So, is there an ideal way to use a website wireframe in the UX design process? In this post we’ll discuss the difference between low fidelity and high fidelity wireframes and why a combination of both can improve your UI/UX design.
What is a low fidelity wireframe?
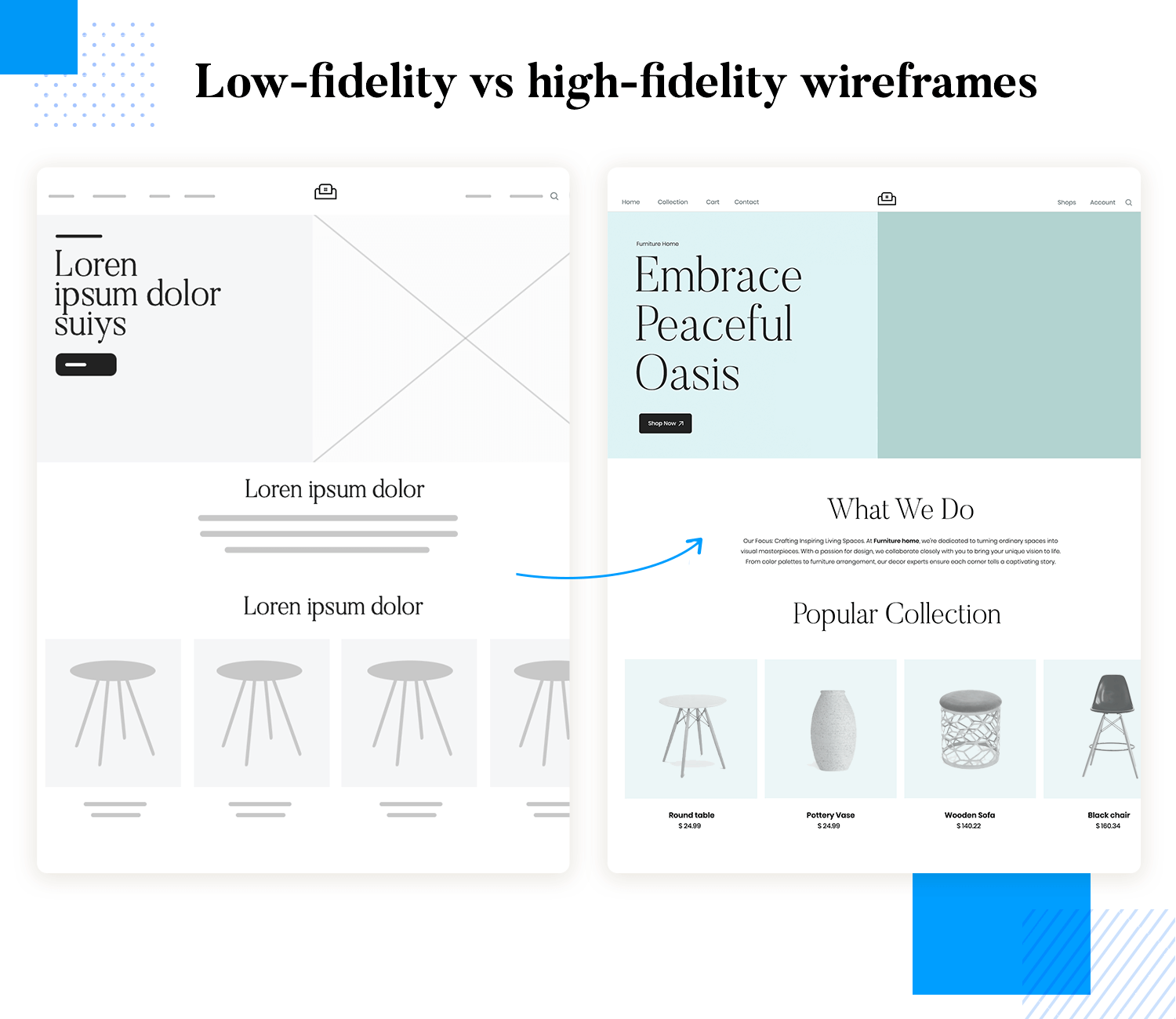
A low-fidelity wireframe is a simple sketch of a user interface that helps you plan out the basic structure and layout of a website or app. These wireframes use basic shapes like rectangles and circles to represent elements such as buttons, text boxes, and images, without worrying about details like colors or fonts.

The main goal is to focus on how everything is organized and how users will interact with it. They’re quick to create, often with pen and paper or basic digital tools, and they include notes to explain what different parts are supposed to do.
When to use low fidelity wireframes and why
You’ll want to use low-fidelity wireframes early in your design process, like when you’re brainstorming ideas or getting feedback from your team or clients. They’re perfect for workshops and initial user testing because they let you explore different layouts and gather feedback quickly without getting bogged down in details. This makes them a cost-effective way to test and refine your ideas before you start adding in the visual design elements.
Brainstorming ideas
You’ll want to use low-fidelity wireframes at the very start of your design process, especially when you’re brainstorming ideas. These wireframes allow you to quickly sketch out different concepts and layouts without committing to any one design. This helps in generating a variety of ideas and exploring different possibilities without spending too much time on each one.
Getting feedback
Low-fidelity wireframes are also useful for getting feedback from your team or clients. Because they are simple and easy to understand, they make it easier for others to provide input on the overall structure and functionality. This feedback can be gathered quickly and easily, helping you to make necessary adjustments early on.
Initial user testing
These wireframes are perfect for initial user testing as they let you explore different layouts and see how users interact with them. You can test the basic navigation and usability without getting bogged down in visual details. This allows you to identify any major issues with the design’s structure or flow before investing time in detailed design work.
Refining
Using low-fidelity wireframes is a cost-effective way to test and refine your ideas. Since they are quick to create and modify, you can make changes based on feedback and testing results without a significant investment of time or resources. This iterative process helps ensure that your design’s structure and functionality are solid before you start adding in the visual design elements.
Advantages of using low-fidelity wireframes
Fast and easy to create
Low-fidelity wireframes can be quickly drawn by hand or with simple digital tools, allowing you to rapidly sketch out different ideas. This speed enables you to explore a wide range of concepts and layouts without spending too much time on any single one. If an idea doesn’t work, you can easily scrap it and move on to another.
Flexibility
Their simplicity makes low-fidelity wireframes highly adaptable. You can quickly iterate on them based on feedback from team members or stakeholders. This flexibility is crucial in the early stages of design, where ideas are still fluid and subject to change.
Focus on functionality
By stripping away detailed design elements, low-fidelity wireframes help you concentrate on the core functionality and user experience. You can focus on how users will interact with the interface and ensure that the basic layout and navigation are intuitive and effective.
Cost-effective
Creating low-fidelity wireframes requires fewer resources compared to high-fidelity wireframes or prototypes. They don’t need specialized software or extensive time investment, making them an ideal choice for the initial stages of development when budgets and timelines are often tight.
Limitations of using low-fidelity prototypes
Using low-fi to map out your UI at the beginning stages does come with its limitations. Being as it’s basically a sketched out storyboard, much is left to the imagination. So you don’t end up feeling discouraged or demotivated by the results of a low-fidelity prototype, read on to know what limitations to expect.
Limitations of low fidelity wireframes
Lack of visual detail
Low-fidelity wireframes are, by nature, simple and lacking detailed visual design elements. This can make it difficult for stakeholders to envision the final product’s look and feel, potentially leading to misunderstandings about the design’s aesthetics and overall impact.
Oversimplification of user experience
By focusing primarily on layout and basic structure, low-fidelity wireframes may oversimplify the user experience, overlooking finer details and nuances of user interaction. This can result in important aspects of the design being missed or undervalued during the initial stages, necessitating more revisions later in the process.
Limited interactive features
These wireframes often lack interactive elements, making it harder to fully test and understand user flows and navigation. Without interactivity, it becomes challenging to spot issues related to user experience and functionality that only emerge when users can engage with clickable prototypes.
By understanding these strengths and weaknesses, design teams can effectively leverage low-fidelity prototypes to create more refined and user-centered high-fidelity designs later on.
What is a high fidelity wireframe?
High-fidelity wireframes are advanced mockups that offer a realistic portrayal of a website or application’s user interface. They include intricate details such as specific typography, color schemes, imagery, and interactive elements like buttons and menus. High-fidelity wireframes often simulate the actual user experience, including hover states, clickable elements, and dynamic content. This level of detail helps in visualizing the final product more accurately and allows for thorough testing of design and functionality.
When to use high fidelity wireframes and why
Detailed design and development
High-fidelity wireframes are essential in the later stages of the design process when you need to work out the finer details of the layout and user interface. They help in refining the design to ensure it meets the desired standards and requirements by specifying exact dimensions, color schemes, typography, and content placement.

Client and stakeholder presentations
When presenting to clients or stakeholders, high-fidelity wireframes offer a clear, detailed, and realistic view of what the final product will look like. This level of detail helps in effectively communicating the design vision and the user experience, making it easier for clients and stakeholders to understand and visualize the end result.
Usability testing
Unlike low-fidelity wireframes, they include detailed design elements and interactions that closely mimic the final product. This allows for more accurate testing of user interactions, navigation flows, and visual elements. Testers can provide feedback on specific aspects like button placements, color contrasts, and overall usability.
Development handoff
High-fidelity wireframes play a crucial role when transitioning the design to the development team. They provide all the necessary details, such as exact measurements, font styles, colors, and interactive elements, ensuring that developers have a clear and precise blueprint to follow. This reduces the risk of misinterpretation and errors during the development phase.
Advantages of high-fidelity wireframes
Realistic respresentation
High-fidelity wireframes offer a detailed and realistic view of the final product, helping stakeholders and team members visualize the design accurately. This clarity aids in better decision-making and alignment on the project goals.
Thorough usability testing
They allow for comprehensive usability testing, including specific interactions, user flows, and visual feedback. This ensures that any usability issues are identified and addressed early, resulting in a more user-friendly product.
Detailed design communication
These wireframes help in effectively communicating detailed design elements to clients, stakeholders, and developers. This ensures everyone involved has a clear understanding of the design vision and reduces the likelihood of miscommunication.
Refined design
High-fidelity wireframes help in refining the design, ensuring all elements are precisely positioned and styled to meet the project requirements. This level of detail leads to a polished and professional final product.
Limitations of high-fidelity wireframes
Time-consuming
High-fidelity wireframes help in refining the design, ensuring all elements are precisely positioned and styled to meet the project requirements. This level of detail leads to a polished and professional final product.
Resource-intensive
They often require advanced design tools and software, as well as skilled designers. This makes them more resource-intensive compared to low-fidelity wireframes, potentially increasing costs.
Less flexibility
Making changes to high-fidelity wireframes can be more challenging and time-consuming, as the design is more detailed and complex. This can make it harder to iterate quickly based on feedback.
Miscommunication potential
If not properly managed, there can be a risk of miscommunication between the design and development teams. If the wireframes are not sufficiently detailed or clear in their specifications, it can lead to discrepancies during implementation.
Key differences between low and high-fidelity wireframes
Detail level
Low fidelity wireframes on a detail level are simple, abstract representations of the design (think sketches) focusing on basic layout and structure without detailed elements. They use placeholders for text and images, providing a rough draft of the interface. High fidelity wireframes, on the other hand, are detailed and polished, closely resembling the final product. They include specific fonts, colors, images, and interactive elements, offering a comprehensive view of the design.
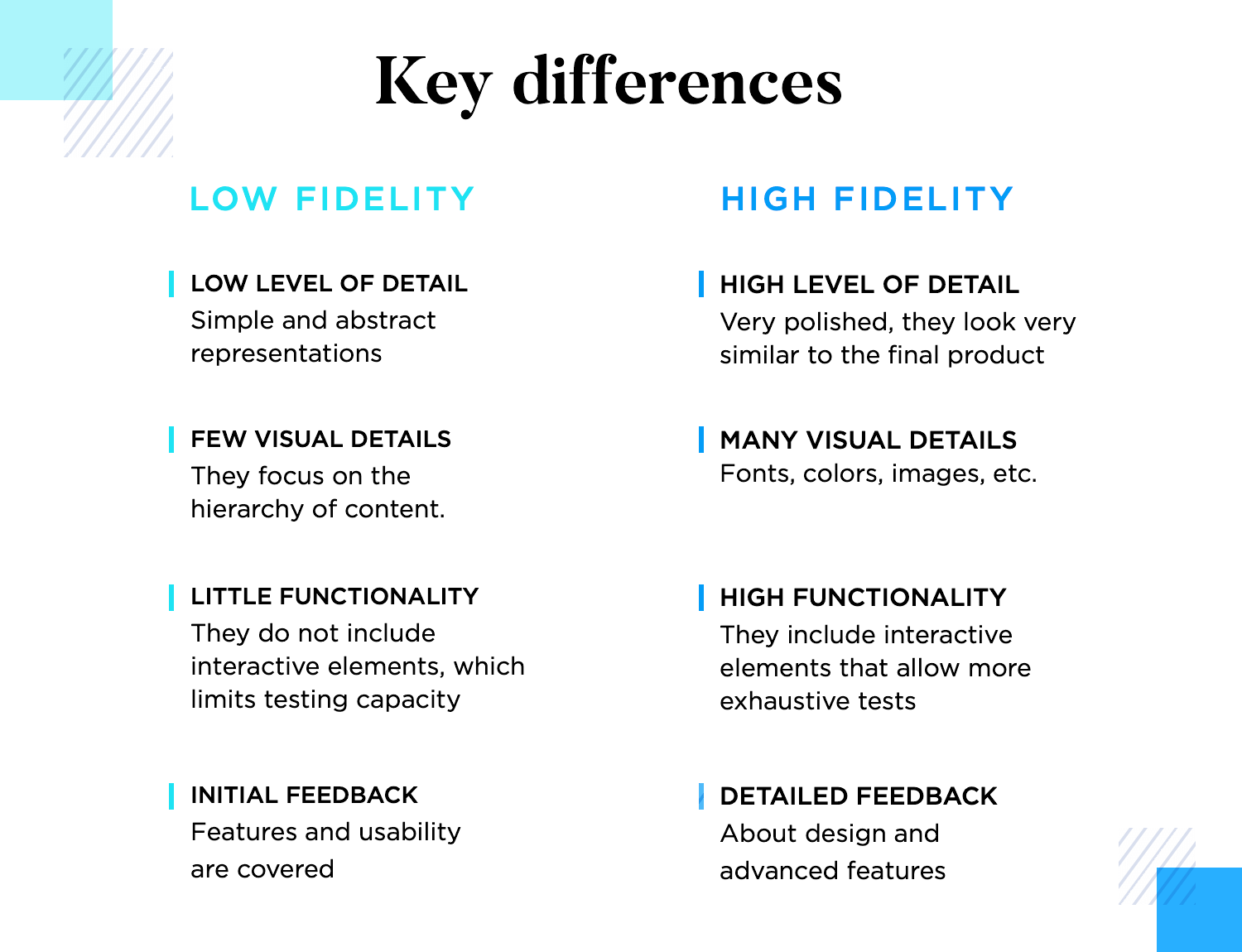
Visual fidelity
Low fidelity wireframes lack visual details and aesthetics, focusing instead on the arrangement and hierarchy of content. This simplicity helps keep the focus on functionality and user experience without being distracted by design details. Whereas high-fidelity wireframes feature high levels of visual detail, including design elements like typography, color schemes, and imagery. They provide a realistic preview of the final product, making it easier for stakeholders to visualize the end result.
Functionality representation
Low-fidelity wireframes typically do not include interactive elements, limiting the ability to test user flows and navigation thoroughly. They are best for initial conceptualization and basic layout planning. However, high-fidelity wireframes often include interactive components, allowing for more extensive testing of user interactions and flows. They can simulate how the user will interact with the final product, providing a more complete understanding of functionality.
User feedback and iteration
The simplicity of low-fidelity wireframes encourages early-stage feedback on core functionalities and usability. Stakeholders and users are less likely to be distracted by visual details, allowing them to focus on the overall experience and structure. High-fidelity wireframes also allow for detailed feedback on both design and functionality. However, they are more suitable for later stages in the design process when it’s time to fine-tune details and interactions based on comprehensive user and stakeholder input.
Design low and high-fidelity wireframes with Justinmind
Use cases for low and high-fidelity wireframes
Low fidelity wireframes
- Brainstorming: Low-fidelity wireframes are excellent for brainstorming sessions as they offer a quick and flexible way to explore design ideas. Their simplicity allows designers to focus on the core concepts without getting bogged down in details, fostering creativity and facilitating rapid iteration.
- Developer buy-in: They can help secure developer buy-in by providing a basic blueprint of the product’s functionality and layout. While not as detailed as high-fidelity wireframes, they still convey the essential elements and interactions, enabling developers to understand the project scope and technical requirements early on.
- Early user testing: These early stage wireframes allow designers to gather feedback on fundamental usability aspects before investing significant time and resources. Their minimalistic design focuses on functionality and flow, making it easier to identify potential issues and refine the user experience iteratively.
- Keeping clients in the loop: They have been proven to be useful for keeping clients informed and involved throughout the design process. By presenting simplified representations of design concepts, clients can provide input and make decisions based on functionality and structure without being distracted by visual aesthetics, ensuring alignment with their goals and preferences.
High fidelity wireframes
- Achieving basic functionality: Use high-fidelity wireframes once the basic functionality of the design has been established. These detailed wireframes include specific UI elements and refined layouts, allowing for a clearer understanding of how the final product will look and operate.
- Testing more advanced interactions: They are ideal for testing more advanced interactions and user flows. High fidelity wireframes provide a realistic representation of the user interface, enabling designers to gather precise feedback on the usability and functionality of interactive elements.
- Handing off design to developers: These wireframes include detailed specifications, visual elements, and interaction guidelines, ensuring that developers have a comprehensive and accurate blueprint to follow during the development phase.
Real-world case studies
1. Low fidelity
The low fidelity wireframe keeps it simple with basic shapes and lines, focusing on where things go rather than intricate details, which is common for early-stage designs. This one shows a work-in-progress route on a map, marking the stops and showing the times accurately.
2. Mobile app paper wireframe
This paper prototype example demonstrates a simple yet effective way to visualize and test user interface designs in a low-fidelity format, allowing for quick iteration and feedback gathering in the early stages of the design process.
3. High fidelity wireframe
The design in this high-fidelity wireframe employs vibrant colors, clear typography, and icons to enhance visual hierarchy and aid in user comprehension. Additionally, the use of realistic data and content suggests a focus on simulating real-world usage scenarios. Overall, the wireframe showcases a polished and detailed representation of a digital product’s UI design.
4. Interactive high-fidelity wireframe
This high-fidelity prototype appears to simulate an e-commerce auctioning platform. The design features a clean and modern layout with various interactive elements, such as dropdown menus, buttons, and checkboxes, suggesting that users can engage with and manipulate data within the interface.